In This Article:
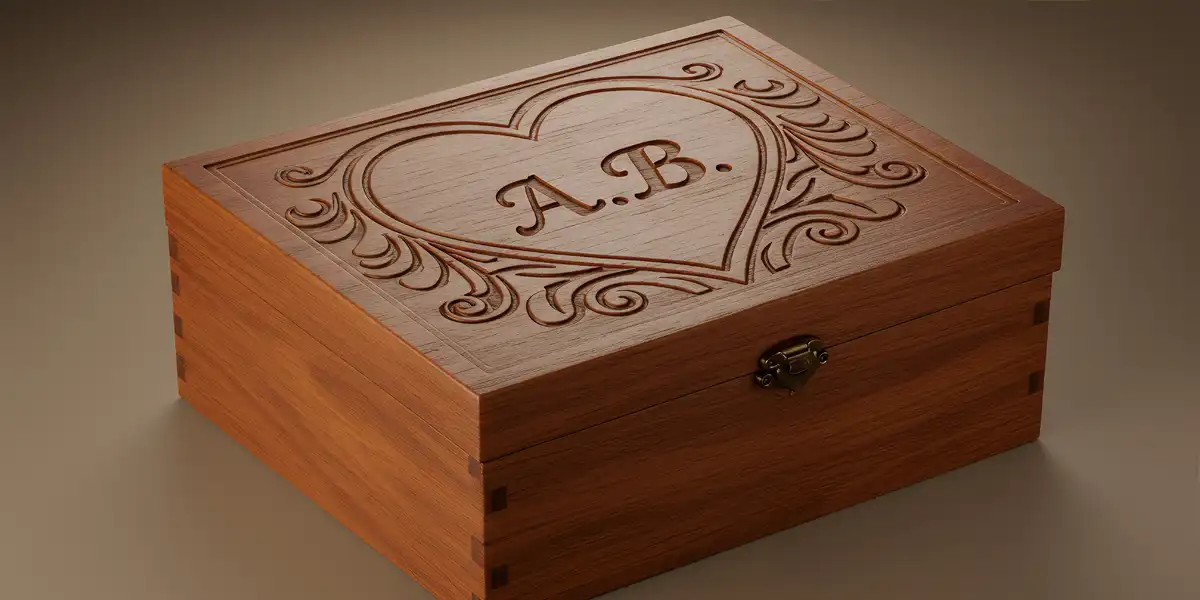
Laser engraving is a high-demand service for ecommerce personalization that blends technology, artistry, and manufacturing to create high-quality, customized products. OWD is the leading 3PL offering Personalized-to-Consumer (P2C) fulfillment services, giving ecommerce brands the ability to allow shoppers to personalize items with custom engravings, embroidery, and direct-to-object printing. It’s the easiest and most profitable way to turn fulfillment into a new revenue-generating opportunity.
But P2C isn’t designed for cheap, mass-produced goods. It’s ideal for businesses looking to elevate their product line with artistic alterations that increase average order values and turn ordinary items into luxury, one-of-a-kind goods designed specifically for each shopper.
Household brands like Nike, LL Bean, Coca-Cola, and Pottery Barn have already integrated product personalization and found wild success, boosting sales and increasing their social media presence.
LL Bean allowed shoppers to personalize tote bags, which reinvigorated the brand and helped it connect with Gen Z and millennial shoppers. Thanks to product customization, #llbeantok has generated 1.5 million views, with #llbeantote close behind at over 900,000 on TikTok.
Nike by You gave shoppers the opportunity to personalize base models with different colors, materials, and patterns and add their initials, favorite number, or a short message. It helped command premium pricing and gave them deeper customer insights into what their target shoppers wanted. In an era where data-driven decision-making is crucial, Nike By You is a goldmine of consumer insights.
The “Share a Coke” campaign launched in Australia and replaced the iconic Coca-Cola logo with popular names. It’s perhaps the best example of product personalization as a natural way to create word-of-mouth marketing and social sharing. More than 500,000 photos were posted on Instagram using the #ShareaCoke hashtag, and Coca-Cola generated 998 million Twitter impressions. More than 150 million personalized bottles were sold globally and Coca-Cola’s market value increased by $1.8 billion during the campaign’s most successful year., making it one of Coca-Cola’s most successful marketing efforts.
If you are interested in the benefits of product personalization and looking behind the scenes to discover what goes into engraving or direct-to-object printing, our Director of Personalization, Ryan Wheeler, shares expert insights so you can understand the artistry and complexity that goes behind producing these luxury goods.
But first, let’s get you caught up to speed on the basics of laser engraving.
What is Laser Engraving?
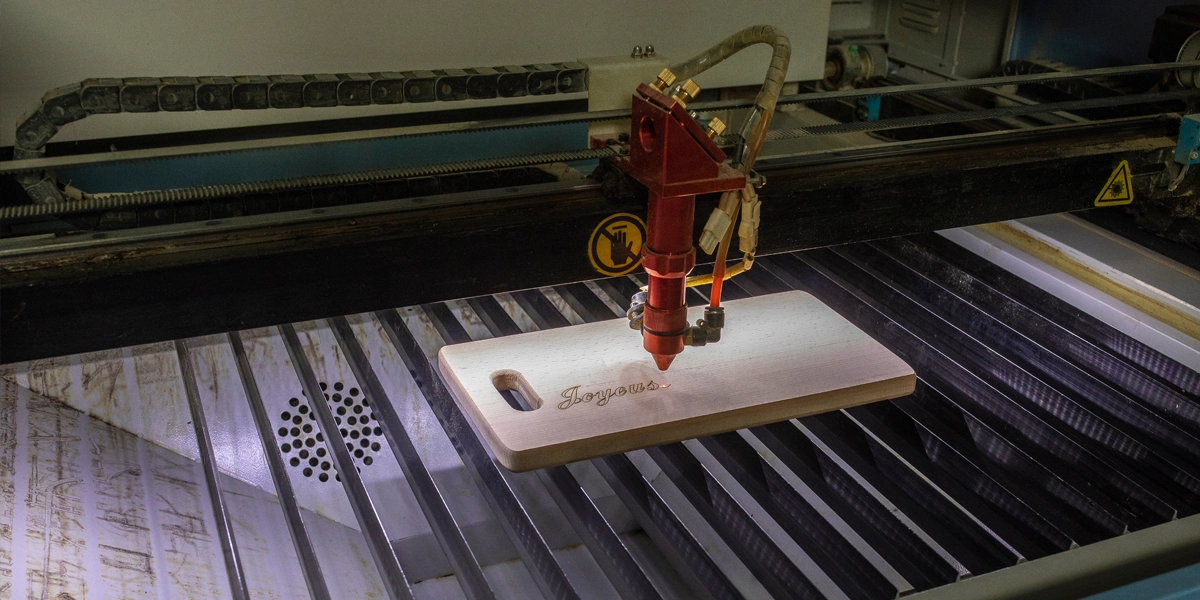
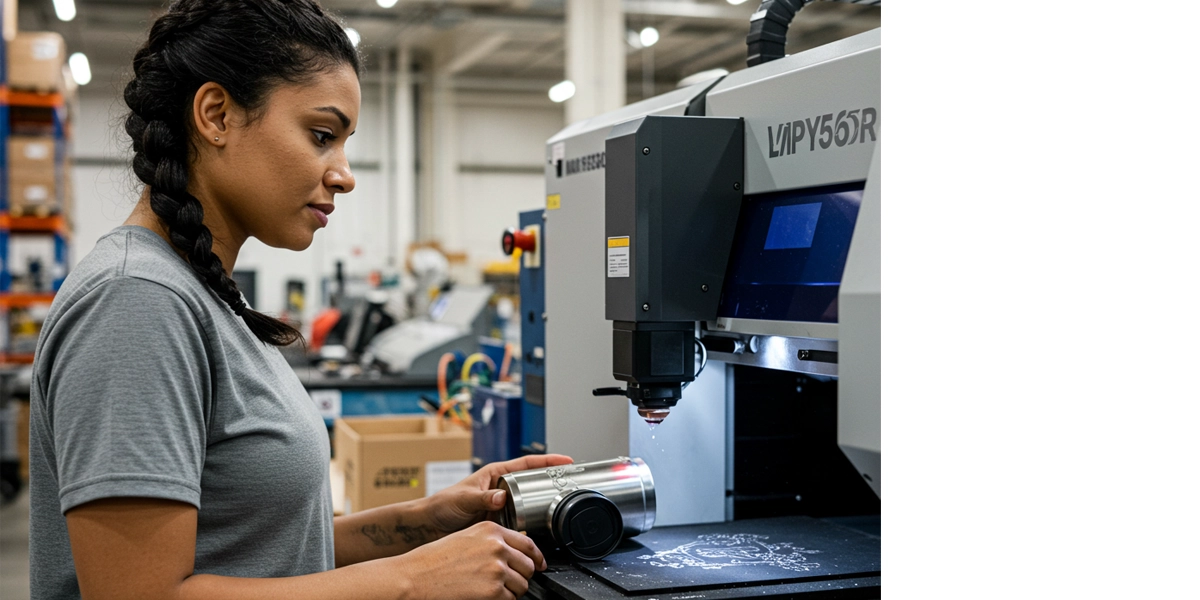
Laser engraving is a precise personalization method that uses high-powered laser beams to remove material from a surface, creating permanent, detailed designs. It is widely used for custom branding, industrial marking, and artistic applications. Unlike traditional methods like rotary engraving or screen printing, laser engraving offers unmatched precision and durability.
How Do Laser Engravers Work?
Laser engravers function by focusing a beam of light onto a material’s surface to vaporize it, leaving behind an etched design. The process involves two primary laser systems:
- Gantry System: Works like a printer, moving in X and Y directions. The laser beam is directed through a series of fixed mirrors and focuses using a lens that adjusts the bed height. Best for larger engravings, moves like a printer, and is slower but precise.
- Galvo System: Uses galvanometric mirrors mounted on servo motors to direct the laser rapidly and accurately, making it ideal for high-speed and high-detail applications. Faster, suitable for small, intricate designs due to its rapid mirror movement.
Different Types of Laser Engravers
Laser engravers vary in technology, each suited for specific materials:
- CO2 Lasers: Gas-based lasers effective on organic materials such as wood, plastic, glass, leather, and acrylic.
- Fiber Lasers: Solid-state lasers ideal for metals and ceramics, offering higher efficiency and faster marking speeds.
- Diode Lasers: Compact and affordable, best for light engraving on soft materials like wood and some plastics.
- UV Lasers: Specialized for marking sensitive materials like glass, plastics, and some metals without excessive heat.
How to Use a Laser Engraver
Using a laser engraver requires careful calibration and testing to achieve the best results:
1. Select the Right Laser and Lens:
The choice of laser and lens determines engraving depth and precision. The lens itself affects the quality. The closer you can get the focal point to the material surface, the smaller the laser dot. A two-inch lens will give you detailed laser results, while a four-inch lens is not as detailed but is also hotter because the focal point is bigger, so you can engrave faster. The most significant factors for producing a quality result are how fast and how much power the laser uses.
2. Adjust Speed and Power:
Slow speeds with high power create deeper marks, while faster speeds allow for lighter etching. Every item is unique, and there is considerable variability based on the material of the item. Think of it like running your hand through a flame—move quickly, and the heat is minimal; slow down, and the heat intensifies. The same principle applies to laser engraving. The slower you go, the more heat builds up, potentially burning the surface. Adjusting speed can create a cooler mark while increasing power produces a hotter mark. Finding the right balance requires the skill of an artisan technician.
3. Test on Sample Material:
Different batches of materials may react differently, so testing ensures consistency. We often request a sample set to deploy test runs and dial in the settings. Once it’s dialed in, OWD sends a photograph to the client for approval and, finally, the finished product so they can examine it in person. Every material reacts differently. Even if you’ve engraved ash wood before using a specific setting, a new batch may produce different results due to variations in sourcing and processing. Since lasers don’t have automatic material detection, testing is crucial to fine-tune settings and ensure consistent, high-quality engravings.
4. Use Fixtures for High-Volume Engraving:
Custom jigs or fixtures are essential for high-volume engraving, ensuring precise placement and optimizing efficiency. These fixtures must be tailored for each item, whether it’s wood, acrylic, or even 3D-printed materials like PLA or PETG. The material choice depends on durability and precision—wood, hardboard, acrylic, and putty are common for traditional jigs, while 3D printing allows for rapid prototyping and adjustments.
Jigs are crucial for consistency and speed. Without them, each piece must be individually measured and aligned, slowing production and increasing the risk of errors. A well-designed jig eliminates this step, allowing for repeatable, high-accuracy engraving. For standard objects like books, built-in machine rulers may suffice, but irregular shapes or engraving in unconventional spots require custom solutions.
Experienced technicians refine jigs quickly, testing and improving designs to maximize efficiency. Some proprietary jigs are developed and stored for future use, helping streamline personalization workflows.
Laser Engraving Materials
Laser engraving is a versatile personalization method that works on a wide range of materials, each requiring specific settings for optimal results:
- Wood: Popular for signage and personalized gifts. The engraving process removes layers of wood, making the design long-lasting and highly durable. However, variations in wood grain and processing can affect the final result, requiring expert adjustments.
- Glass: Used in dinnerware and decorative pieces. The laser creates a frosted effect, adding a premium look to glassware and plaques.
- Metals: Ideal for industrial marking and jewelry engraving. Some metals require pre-treatment, such as anodizing or coating, to enhance visibility.
- Plastics: Great for branding and identification. However, certain plastics, like PVC, are unsafe for laser engraving as they release toxic, acidic fumes that can damage equipment and pose health risks.
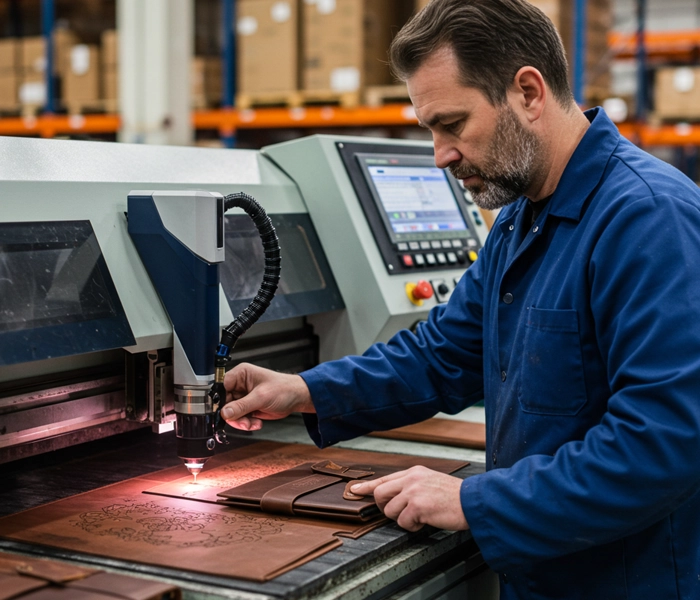
- Fabric & Leather: Engraving fabric creates unique textures, while leather engraving results depend on whether it’s genuine or synthetic. Real leather engraves well, but faux or vegan leather can produce inconsistent results, potentially melting or emitting an unpleasant odor if it contains polyester.
Clothing Laser Engraving
Laser engraving on fabric burns away the top layer of fibers to create striking, permanent designs. This technique is commonly used for:
- Denim customization: Produces a worn, vintage look by singeing the fabric.
- Leather branding: Works well on genuine leather but requires testing on synthetic variations.
Comparing Laser Engraving to Other Personalization Methods
Each personalization method has trade-offs in durability, cost, and efficiency:
Laser Engraving | Direct-to-Object (DTO) Printing | Embroidery & Fabric Printing |
|---|---|---|
The design is physically etched into the material, making it the most durable option, especially for wood, metal, and glass. Unlike printed methods, it won’t crack, fade, or peel over time. | Uses a gantry system similar to a laser but prints ink directly onto rigid surfaces. A UV light follows the print head to cure the ink instantly. While visually detailed, DTO prints on plastic and other smooth surfaces can wear away over time. | Embroidery provides a raised, textured effect but isn’t suitable for all fabrics. Direct-to-film (DTF) or heat transfer printing works like silk screening, applying ink via a heat press. These methods are cost-effective for apparel but may crack or fade with wear. |
How to Laser Etch Wood
Wood laser etching involves adjusting power and speed to create different depths and shades. Some woods, like ash or oak, may require multiple passes to achieve the desired result.
Laser Etching Fabric
Laser etching fabric offers a burned-in look, often used for high-end fashion or decorative elements. Different fabrics respond uniquely, requiring careful power adjustments to prevent burning through the material.
Comparing Laser Engraving to Direct-to-Object Printing
Direct-to-object (DTO) printing applies ink directly to rigid surfaces using a gantry system, similar to inkjet printing. However, DTO prints can wear off over time, whereas laser engraving is permanent.
Key Factors for Laser Precision
Achieving high-quality engraving depends on:
- Speed vs. Power: Slower speeds allow deeper engraving, while higher speeds offer efficiency.
- Lens Choice: A 2-inch lens provides fine details, while a 4-inch lens covers larger areas faster.
- Material Testing: Different materials react differently to laser settings, requiring adjustments for consistency.
Challenges in Large-Scale Personalization
Maintaining consistency across thousands of products requires:
- High-quality machinery and maintenance.
- Skilled technicians to fine-tune settings.
- Batch processing using templates for precise placement.
Inside the World of Laser Engraving: An Interview with OWD’s Director of Personalization, Ryan Wheeler
Q: What do you enjoy most about laser engraving?
Ryan: “The versatility. Whether it’s engraving a delicate piece of jewelry, branding leather goods, or marking industrial parts, the applications are endless. Plus, the technology is always evolving, which keeps things exciting.”
Q: Can you explain how a laser engraver works?
Ryan: “Sure! A laser engraver uses a high-powered beam of light to remove material from a surface, leaving behind a permanent mark. Depending on the type of laser—CO2, fiber, diode, or UV—the machine can engrave different materials like wood, metal, acrylic, and even fabric. The process is controlled by software that directs the laser with pinpoint accuracy, allowing for intricate designs and consistent results.”
Q: What’s the difference between laser engraving and laser etching?
Ryan: “Laser engraving removes material to create deep cuts, while laser etching slightly alters the material’s surface without significant depth. Engraving is great for durability and long-lasting marks, whereas etching is used more for lighter, high-speed applications like barcodes or serial numbers.”
Q: What are the most common materials used in laser engraving?
Ryan: “Wood is a big one—people love the rustic, natural look. Metals, especially stainless steel and anodized aluminum, are popular for industrial and promotional items. Acrylic is great for signage because it engraves cleanly, and leather is another favorite for custom goods. Each material reacts differently, so knowing how to adjust the laser settings is key.”
Q: Any tips for getting the best engraving results?
Ryan: “Always test your settings on a scrap piece before engraving the final product. Different materials require different power and speed settings. Also, keep your lenses clean and maintain your machine regularly to ensure optimal performance.”
Q: What challenges do laser engravers face?
Ryan: “Scaling production while maintaining quality is a big one. Also, competition is growing, so offering unique designs and excellent customer service is essential. Keeping up with technological advancements is another challenge, but it’s also what makes the industry exciting.”
Q: What’s the biggest challenge in maintaining consistency across thousands of personalized products?
Ryan: Calibrating and maintaining the machinery. This is a premium option that requires patience and care. We’re a very conscientious company and our most successful clients are people who really care about products. They care about how they look and have the patience to go through the process.
Q: What’s the biggest challenge in maintaining consistency across thousands of personalized products?
Ryan: “Calibrating and maintaining the machinery. This is a premium option that requires patience and care. We’re a very conscientious company and our most successful clients are people who really care about products. They care about how they look and have the patience to go through the process.”
Q: How do you balance speed and detail when engraving high-volume orders?
Ryan: “Efficiency in high-volume engraving comes down to two key factors: the size of the engraving and the depth of the mark.
To optimize speed, we use fixtures and batch processing. For example, if we need to engrave multiple small items, we can laser-cut a custom acrylic jig that holds 50 pieces in a tray. This allows us to place the entire tray in the machine at once, ensuring precise alignment and consistency while significantly increasing throughput.
The engraving size plays the biggest role in determining speed. A small logo in the corner of a book cover takes far less time than engraving the entire face of the book. Depth is the next critical factor—deeper engravings require either slowing the laser down or making multiple passes, both of which add time to the process.
By strategically balancing batch processing, fixture design, and engraving parameters, we achieve both speed and high-quality detail without compromising efficiency.”
Q: Where do you see the laser engraving industry heading?
Ryan: “I think automation and AI-driven design tools will play a bigger role in streamlining the process. Customization is in high demand, and businesses are looking for faster, more efficient ways to personalize products. I also see an increase in eco-friendly materials and sustainable engraving practices, which is an excellent direction for the industry.
Obviously, the most sustainable way to engrave something is by hand but it’s not a practical or scalable option. Although the machinery requires power and rare metals, the process of engraving uses heat to remove material from the item rather than adding inks or solvents. The fact that you’re not adding anything makes it a sustainable, eco-friendly offering.”
Boost Sales, Brand Awareness, and Your Entire Product Line with P2C Fulfillment
Creating unique, artisan, personalized goods requires an expert touch. It’s not only a matter of investing in expensive machinery. Skilled technicians are essential to manage the personalization process from start to finish.
Fortunately, OWD is the only 3PL offering comprehensive fulfillment services to help you lower logistics costs while opening up new profit centers with P2C fulfillment. On top of providing the standard logistics services, such as inventory management, reverse logistics, and order management, we also deliver unique additions you won’t find from other 3PLs like Shipbob or Amazon FBA.
Deliver world-class customer support with our ecommerce call center services. Since 2001, we’ve been helping our clients deliver excellent customer service by handling their calls, e-mails, and chats with only American agents.
Use our outsource fulfillment services to compete with big retailers like Amazon and Walmart. We have three fulfillment center locations in California, South Dakota, and Ohio so you can reach 99% of the U.S. shoppers in two days. Convert more shoppers with same-day or overnight shipping and gain transparent rates with our flat-rate shipping pricing.
Most importantly, utilize P2C fulfillment and start offering product personalization. Whether it’s laser engraving, embroidery, or direct-to-object printing, boost profits and elevate your brand with seamless product customization. Create the best unboxing experiences with custom packaging options and personalized greeting cards.
Schedule a complimentary logistics consultation to discover inefficiencies in your fulfillment strategy and how you can start offering world-class personalization with OWD. We’ll handle storing, creating, and fulfilling all orders while you can focus on other strategic initiatives. We hope to chat with you soon!
In This Article:
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Tincidunt urna mauris eu quam vulputate lobortis sit. Purus feugiat arcu nunc quisque massa ut.